Products >> Titanium >> Titanium forge
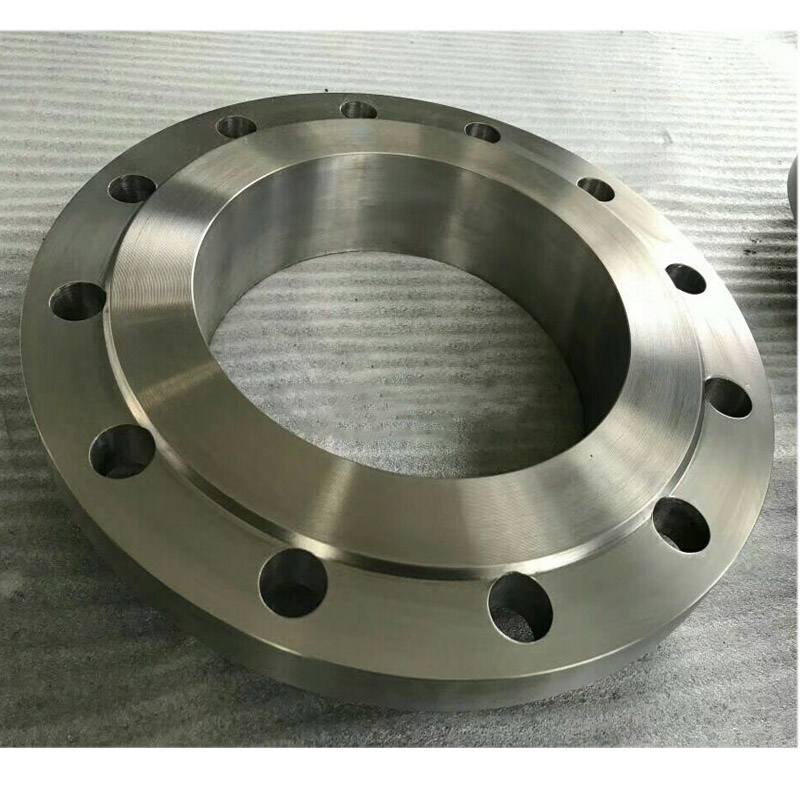
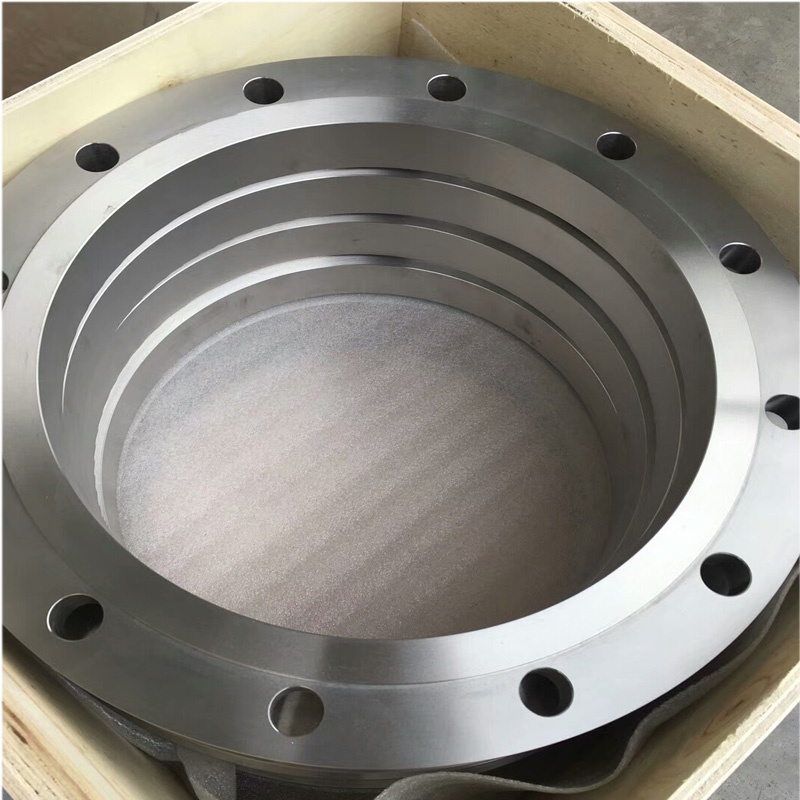
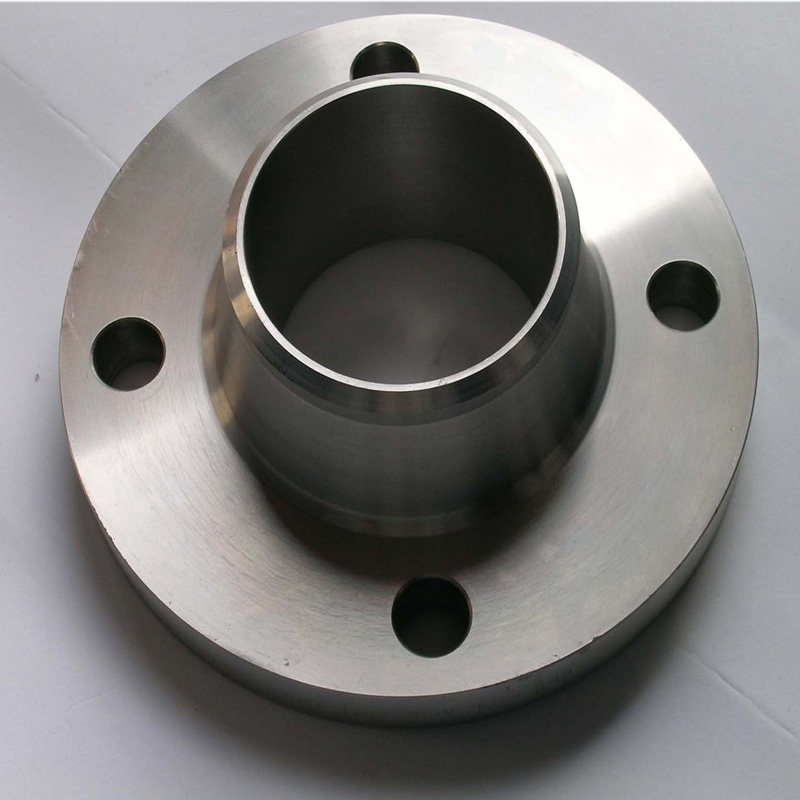
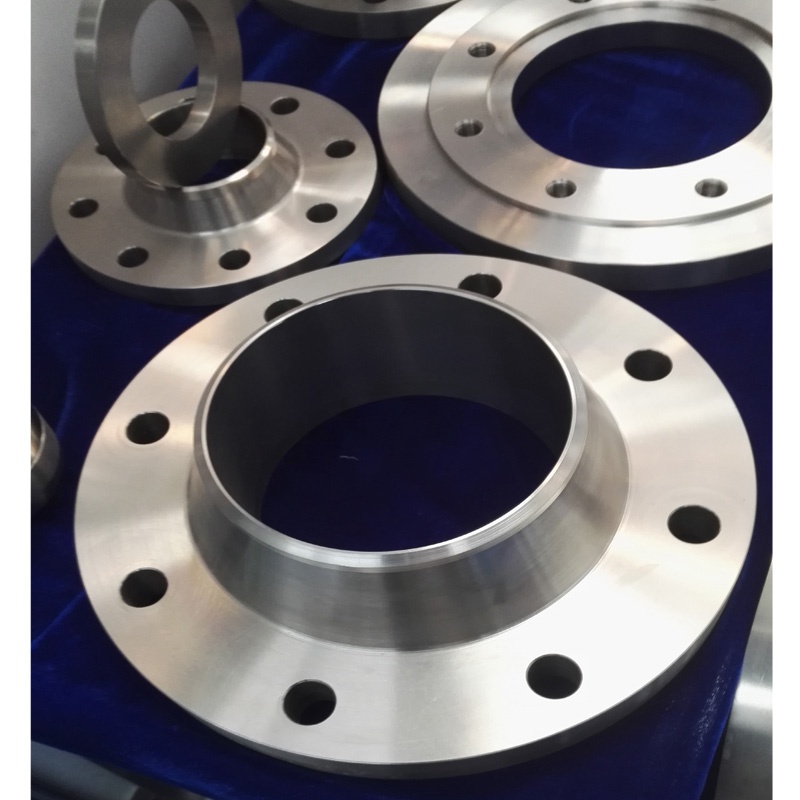
Titanium welding-neck flange
- Product No.:2023911145028
- Material Grade:Titanium alloy
- Size:1/2 inch to 48 inches
- Test:PMI, UT
According to ASME B16.5, the standard dimensions for titanium welding neck flanges (also known as WN flanges) are as follows:
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS): 1/2" to 24"
- Flange Class Ratings: 150, 300, 400, 600, 900, 1500, and 2500
- Flange Facings: Raised Face (RF), Flat Face (FF), Ring Type Joint (RTJ)
- Flange Materials: Titanium (grade 1, 2, 5, 7, 12), with the grade specified based on the application requirements
The dimensions for titanium welding neck flanges, such as outside diameter (OD), bolt circle diameter (BCD), neck diameter (ND), and thickness (T), vary depending on the nominal pipe size and the flange class rating.
Manufacturing titanium welding neck flanges usually involves three main steps. These include:
Prep Step: Acquire high-grade titanium material (typically bars or plates), clean or treat its surfaces to remove impurities, and perform any required surface treatments in order to clean off impurities from it. Flange Design: Determine required dimensions, welding neck length, class rating and facing type (RF, FF or RTJ) depending upon application requirements and ASME B16.5 standards. Cutting and Shaping: Use cutting techniques such as sawing or shearing to transform titanium material into the ideal shape and size for the flange, such as drilling out an opening for pipe passage and creating the neck of the flange. Turning and Machining: Incorporating turning and machining processes can help refine dimensions, smooth surfaces and meet precise tolerances more precisely than other means can. These operations might include facing, chamfering, drilling bolt holes or beveling welding ends - among many others. Heat Treatment: When necessary, subject the titanium flange to heat treatment processes such as annealing or stress relieving to enhance its mechanical properties and alleviate residual stresses.
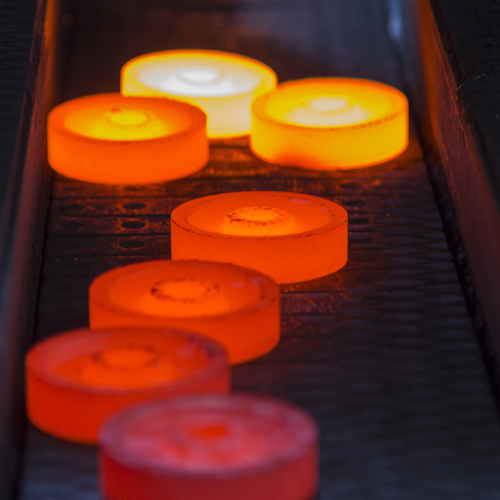


Welding: For better flange connection and reduced contamination risk, using TIG welding techniques such as Tungsten Inert Gas welding may be used to successfully join its neck to its body. Titanium requires specialist expertise for proper penetration and contamination-free welding procedures.
Surface Finishing: Apply surface finishes and coatings such as passivation or corrosion-resistant finishes to shield titanium flanges against environmental and chemical damages.
Inspection: Carefully examine a completed titanium welding neck flange to make certain it conforms with all specifications, quality standards, and industry regulations. This may involve nondestructive testing such as visual inspection, ultrasonic testing or dye penetrant testing - including non-destructive techniques like nondestructive testing (NDT). Certification and Documentation: Obtain appropriate paperwork such as material certificates, test reports and compliance with ASME B16.5 standards to validate and traceability of titanium welding neck flange.
Contact Us

Name: Mr. Ren
Tel: +86-18292471213
E-mail: info(at)intemetal.com
Add: Middle Section Baotai Road, Weibin District, 721013, Baoji, Shaanxi Province, China